
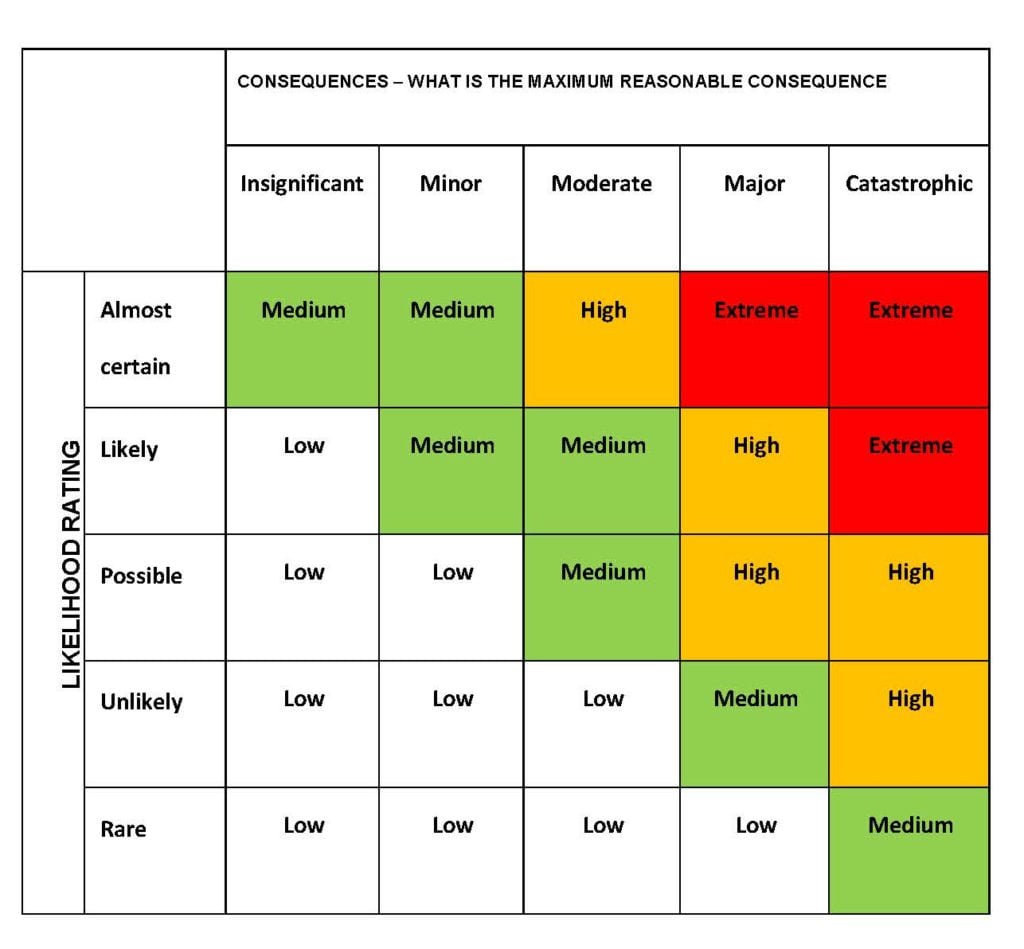
4 Risk Assessment Methods Using Impact and Probability.All these methods, though beneficial for management, have their limitations and drawbacks. There are other, quantitative methods for analyzing risks, such as Sensitivity analysis, Expected Monetary Value analysis and Monte Carlo Simulations. The Impact and Probability Matrix is a simple and easily understood method of prioritizing risks and allocating resources. These are often referred to as Impact and Probability Matrix and can take both qualitative and numerical values. A commonly used method for risk assessment is preparing descriptive scales to rank risk in terms of probability and impact. There are various aspects of the project that can be affected by a risk event, such as cost, safety, operation, quality, etc. By combining the probability and impact, the Level of Risk can be determined. The probability is the likelihood of an event occurring and the consequences, to which extent the project is affected by an event, are the impacts of risk. In risk analysis, risk is traditionally defined as a function of probability and impact. Initially, qualitative methods are used to examine, categorize and determine the main risk events identified, which are relevant for a more detailed quantitative assessment. The risk analysis is a two-stage assessment process. Risk management involves identifying possible risks and analyzing their potential in order to respond to and control the projects most significant threats and opportunities. Therefore, Risk Management is an important part of any organization as proper management increases the likelihood for the success of a project. All projects are unique and thus the associated risk varies between projects. Risks are events caused by uncertainties, which can have a positive or negative effect on the project objectives. Looking at impact versus probability is common in order to categorize and prioritize risks as some risks may have a severe impact on projects objectives but only happen on rare occasions, while other have a moderate impact but occur more frequently.Īll organizations activities involve risk. The example below is hypothetical.Impact and probability are the two main components of Risk analysis. You do so by dividing the event into parts and assessing the individual levels of severity, with their associated probability. Nonetheless, the worst possible outcome can be emphasised if deemed appropriate. In such a case, it is important to introduce risk-reducing measures as quickly as possible.Īs a main rule, the probability of the worst possible outcome is low, and other outcomes are more probable. We may also come across examples of undesired events that are both very probable and could have severe consequences. This does not mean that it is wrong to envisage the worst possible outcome, and it can often be appropriate to show that an activity may have very serious consequences. It is therefore important to adapt probability to the outcome. It is important to remember, in this regard, that the probability of the worst possible outcome will often be lower. The criteria for consequence provide a definition of these categories of consequences in relation to our values.Īn undesired event may have several different consequences of varying severity, and it is easy to think of the worst possible outcome of events when carrying out a risk assessment. The categories of consequences for each value are as follows: We assess consequence in relation to our different values: One event can have several different consequences. Consequence assessmentĬonsequences are the possible outcome of an undesired event, and may involve loss of or damage to values we want to protect.Ĭonsequence is estimated by first imagining the outcomes of an undesired event. We recommend using former experience of the same or similar events, and discussing these in groups to discover what aspects are deemed probable. It is also possible to omit the estimation of probability, but you must always provide reasons for this in the report.Įstimate probability using the criteria to the best of your ability, it is not expected that you will be able to see into the future. This should be noted in the report for the risk assessment. This will impact how the event is plotted in the risk matrix, and may illustrate risk that is unrealistically high or low. The range of frequency may be too extensive, e.g., for events that occur relatively frequently, or too limited for events that occur very rarely. Sometimes, the probability criteria we use at the University of Bergen will not be the right fit for your risk assessment.

Between once every 5 years and once every 10 years.īetween once every year and once every 5 years.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
